Among the diseases of the periodontium, the one that affects most people is gingivitis.
This inflammation can be acute or chronic. Acute inflammation occurs when we injure, puncture or burn our gums, usually locally in an area of our oral cavity.
Sudden flare-ups of inflammation often occur during the eruption of a wisdom tooth when it is already half erupted.
This is because there is a “pocket” in the gum next to the crown of the semi-pre-fractured tooth, which is formed as part of tooth development. If this pouch starts to move with the oral cavity, its location means that it cannot be cleaned properly, and bacteria start to multiply as food debris gets in, leading to inflammation.
Main symptoms: swollen, bloody, red gums around the tooth; pain; bad breath. In more severe cases, you may develop pus, difficulty swallowing, and oral obstruction, which you should see your dentist to prevent!

(image source : greatartdesigns.com)
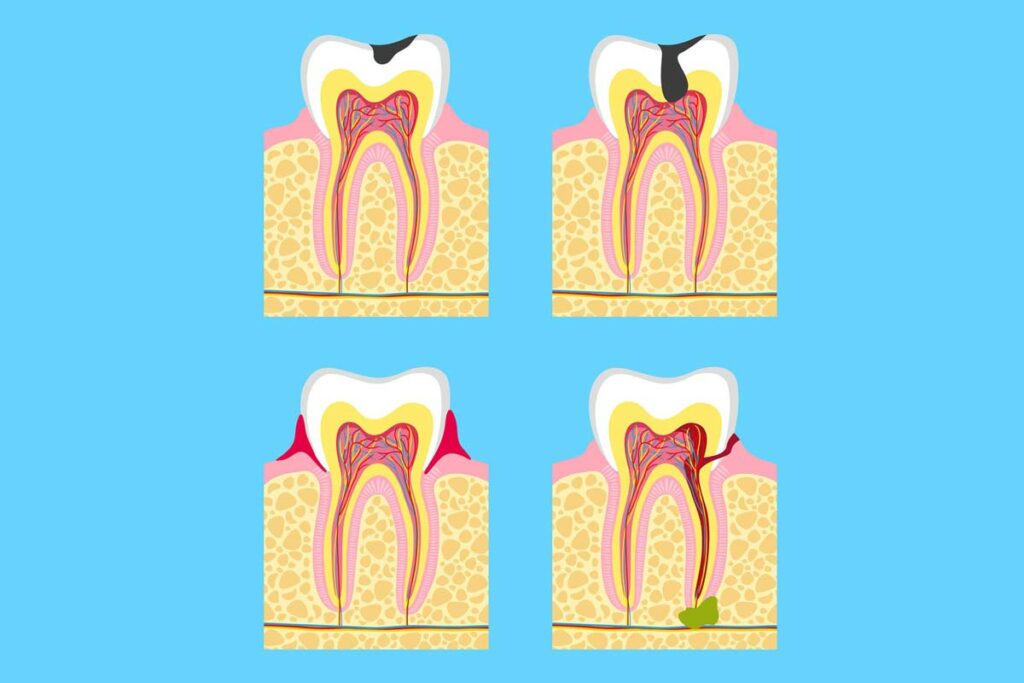
Chronic gingivitis most often develops as a result of tartar build-up.
If this is not removed, the inflammation will spread to the deeper parts of the periodontium and destroy the supporting structure of the teeth.
It is characterised by a pouch formed by tissue destruction, which can cause very unpleasant pain. The bag contains plaque and the deeper spread of bacteria can lead to tooth loosening.
Besides poor oral hygiene, smoking and alcohol consumption can be predisposing factors. This can be aggravated by internal medical conditions, such as diabetes; or by taking certain medicines.